Visiting the court
Information that service seekers coming to court should know. –
Identify whether the type of case they are coming to is civil,
criminal, or tort.
Before going to court, it is essential to identify the case type, as this will determine the legal procedures, rules, and court handling the matter. Case types can range from civil to criminal, family to probate, and each has its own specific requirements and processes.
Before heading to court, it's crucial to check your appointment to ensure everything is in order. This means confirming the date, time, and location of your hearing or trial.
Before going to court, it's essential to get your registration number, as this is a unique identifier for your case. The registration number is typically provided when you file your case or receive your court summons, and it helps the court and relevant authorities locate your file quickly.
Before going to court, it’s crucial to present all necessary documents to support your case. These documents may include contracts, evidence, identification, court filings, witness statements, or any relevant paperwork that backs your claims or defense. Ensuring you have all required documents organized and complete can significantly impact the outcome of your case. Missing or incomplete paperwork can lead to delays, complications, or even dismissal of your case.
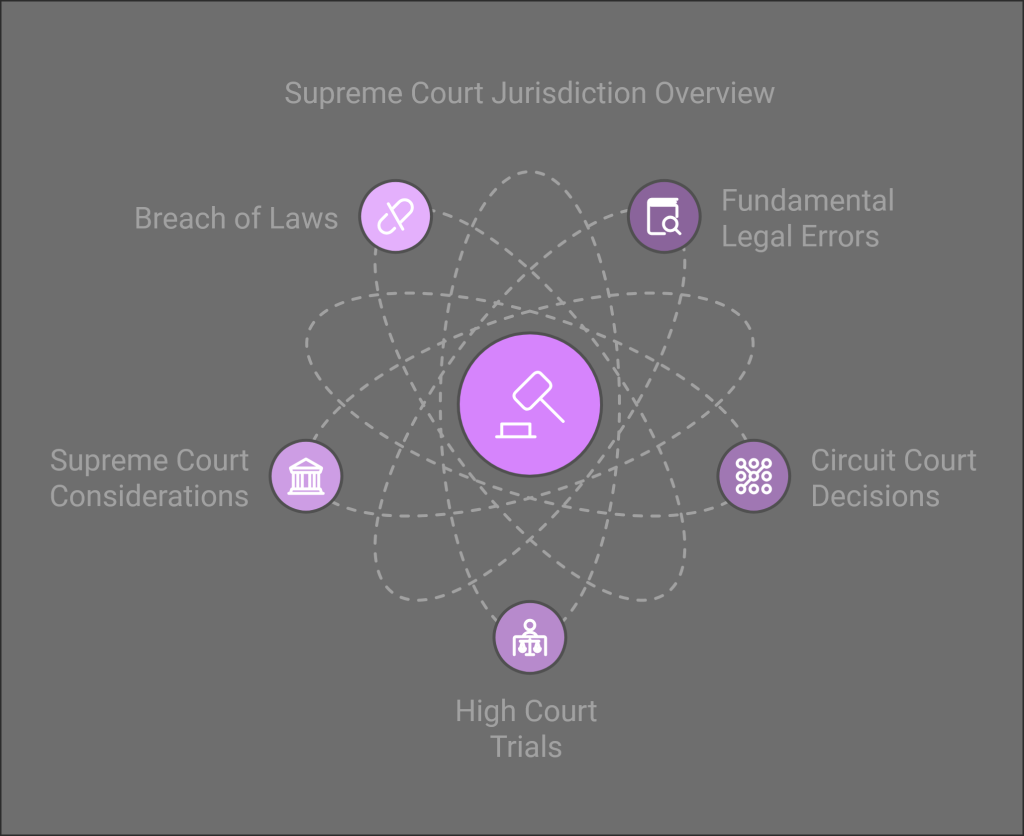
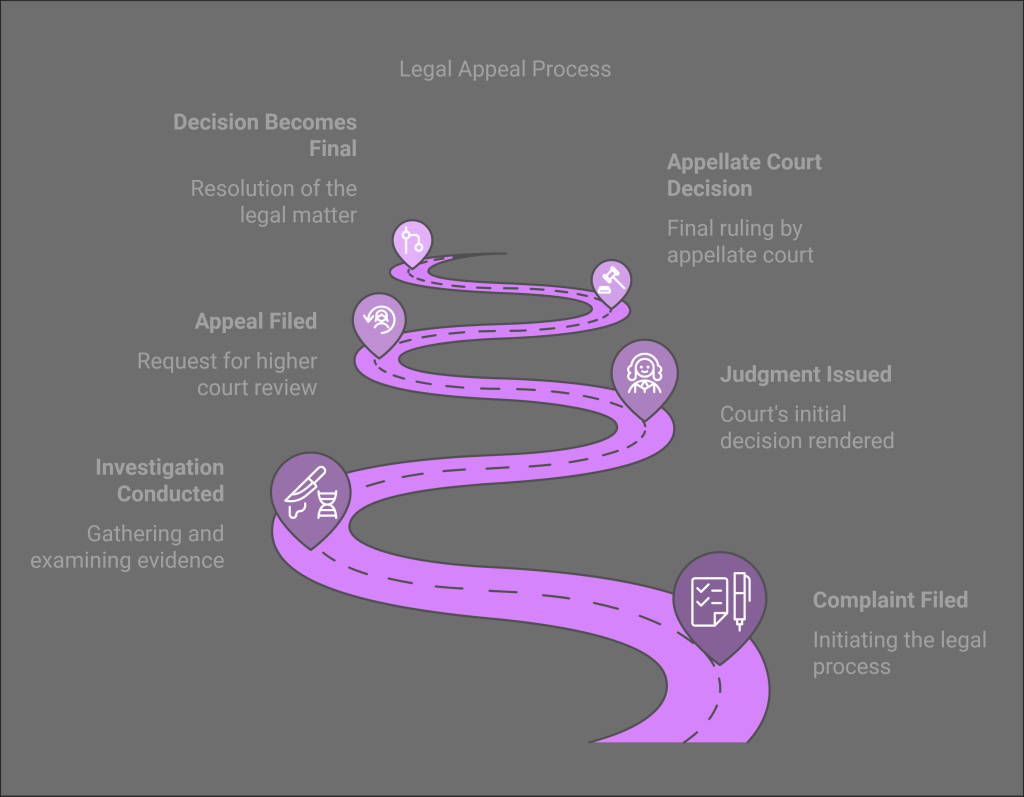
About the appeal system
The Amhara National Regional State Supreme Court has a rich history rooted in Ethiopia’s long-standing legal traditions and commitment to justice. As one of the pillars of governance in the Amhara region, the court system has evolved over the years to uphold the rule of law, protect human rights, and ensure fair judicial processes for all citizens.
Our judicial system traces its foundations to Ethiopia’s ancient legal customs, including the Fetha Negest, which served as a primary legal code for centuries. With the formation of the modern Ethiopian legal system, the Amhara Supreme Court was established to oversee the region’s judiciary, providing legal interpretation, ensuring due process, and maintaining checks and balances within the justice system.